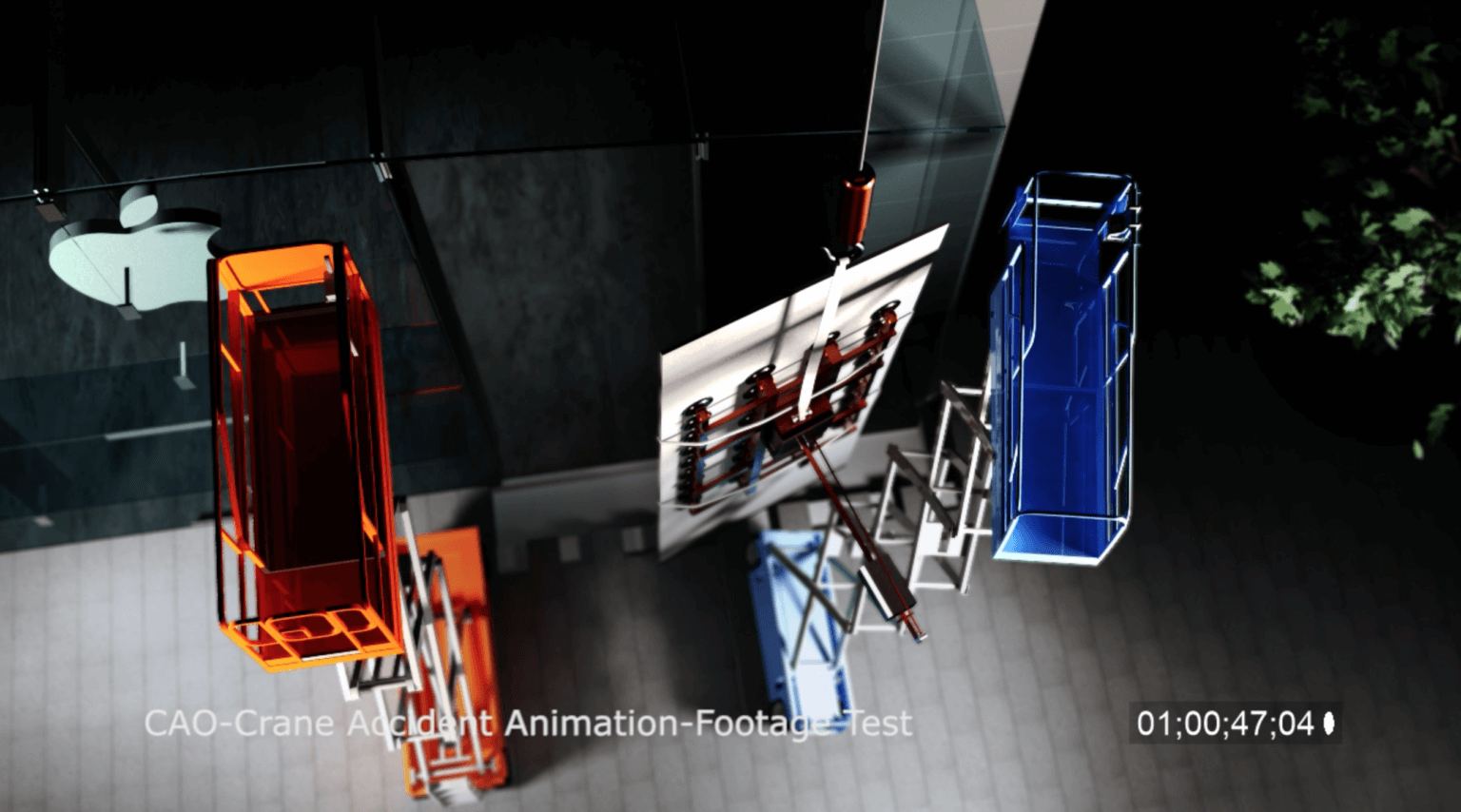
oil & gas animation
In 1991, Beauty and the Beast became the inaugural animated film to receive a nomination for the esteemed Best Picture category. Subsequently, Up (2009) and Toy Story 3 (2010) also earned nominations in this category when the academy increased the number of nominees from five to ten.
In the realm of animation, there has long been a strong connection to comic books. While it is common for numerous comic book characters to transition onto the screen, particularly in Japan where many manga series are adapted into anime, there is also frequent integration of original animated characters within comic books and magazines. In a somewhat comparable manner, video games (which are an interactive form of animation that has developed into its separate medium) have drawn inspiration from movies in terms of characters and storylines, and the reverse is also true.
In addition to receiving Academy Awards for Best Animated Short Film (since 1932) and Best Animated Feature (since 2002), animated films have been frequently recognized and honored in various other categories, notably including Best Original Song and Best Original Score.